Over a million people are diagnosed with skin cancer, or melanoma, each year, and many will share the same emotions: Why me? Am I in serious danger? What should I do? There is no need to panic. Skin cancer is not necessarily life threatening, nor does its therapy have to be disfiguring; however, if left untreated, the disease can continue to progress.
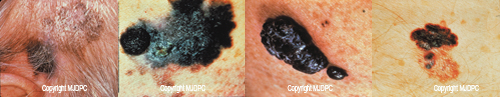
Anyone can get skin cancer. Your risk of developing skin cancer is increased if your parent, child, or sibling has had melanoma. Redheads and blondes have a two-fold to four-fold greater risk of developing melanoma. Darker-skinned people have more melanin, or brownish pigment, in their skin which serves as a buffer by absorbing the sun's harmful ultraviolet rays; thereby lowering, but not eliminating, the risk of skin cancer. Even though there is a strong correlation between ultraviolet exposure to the sun and all types of skin cancer, you can still get skin cancer even if you stay out of the sun.
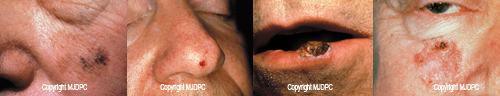
Warning Signs
Most moles develop sometime after birth, but some people are born with moles. "Birth moles" increase a person's risk for melanoma. The development of a new mole or any changes in the size, color, shape or texture of a mole may be a sign of skin cancer, and should be reported to a dermatologist right away. Melanomas can develop anywhere on the body, even in places that are not exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet.
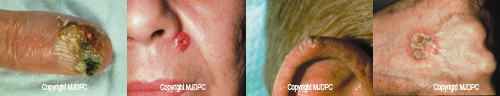
Types of Skin Cancer
There are three main types of skin cancer:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Malignant Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer and represents about 80% of new skin cancers. This type is rarely life threatening and does not spread. They can be inherited, but usually occur in patients who have had repeated sun exposure. Patients that develop a Basal Cell cancer have a 60% chance of developing another one within 5 years.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma is another common type of skin cancer that is rarely life threatening. It represents about 16% of new skin cancers and is found most often in people with fair complexions. This type may develop from an Actinic (Solar) Keratosis which is a scaly, crusty bump on sun-damaged skin. They can appear as a red bump, or may seem like an ulcer. They may also seem like a sore that just won't heal. They can range in size from a few millimeters to a few centimeters in diameter.
Malignant Melanoma represents only about 4% of newly diagnosed skin cancers. It is the most serious form of skin cancer and can be deadly. However, if treated early while it is still flat and thin, the cure rate is about 95%. If it is allowed to grow and become lumpy, it can be fatal. This cancer usually stems from a mole that has been present for many years. If you have a mole that doubles in size in just a few months, you should have it examined by a specialist immediately.
There are many treatment options available for skin cancer including scraping and burning, freezing, radiation, routine excision and Mohs surgery. It is necessary to consider all the benefits and drawbacks of the various procedures when you choose your treatment. Often the cancer cells \n visible to the eye may extend beneath the surface of the skin. These cancer cells must be completely removed or they can lead to regrowth and recurrence of the tumor.
Mohs Micrographic Surgery
Mohs does not rely only on what is seen. Mohs surgery combines the surgical removal of the tumor with the immediate microscopic examination of the tumor and underlying diseased tissue. Our doctor performs Mohs surgery for patients in our region to identify, remove and examine the entire tumor and roots layer-by-layer until the cancer is completely gone. Mohs surgery provides the highest cure rate, has the lowest chance of regrowth, minimizes the potential for scarring or disfigurement and is the most exact and precise means of removal.
Mohs surgery is effective for most types of skin cancer and is commonly used to treat Basal and Squamous Cell Carcinomas. It is the treatment of choice for recurring cancers, large cancers, cancers where the edges cannot be clearly defined, or in areas where it is important to preserve healthy tissue for the maximum functional and cosmetic results.
After our doctor performs your Mohs surgery, your risks of skin cancer can be reduced when you protect yourself from the sun, are aware of suspicious growths and visit your doctor for regular check-ups.
Find out if you could benefit from this procedure. Schedule your consultation with our practice today.